Gynecomastia, the enlargement of breast tissue in men, is more common than many people realize. Although it’s usually benign, gynecomastia can be a source of physical discomfort and emotional distress.
Fortunately, advancements in cosmetic surgery have made effective treatment more accessible and achievable.
What Causes Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia often stems from hormonal imbalances, where estrogen levels rise or testosterone levels fall, leading to an increase in breast tissue. Here are some common factors that contribute:
Hormonal Shifts: Puberty and aging both bring natural hormone changes, which can cause temporary gynecomastia in adolescent boys and persistent cases in older men.
Medications: Certain medications—like anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, and some antidepressants—can disrupt hormone levels and lead to breast tissue growth.
Medical Conditions: Conditions affecting liver or kidney function, thyroid imbalances, or obesity can influence hormone levels and contribute to gynecomastia.
Lifestyle Factors: Alcohol, marijuana, and anabolic steroids have been linked to increased estrogen production, which can contribute to gynecomastia.
Non-Surgical Options for Treating Gynecomastia
Not all cases require surgery. Here are some non-surgical options to consider:
Lifestyle Changes: Reducing alcohol, avoiding recreational drugs, and managing weight can help, particularly if the condition is linked to lifestyle factors.
Medication: Anti-estrogens or hormone regulators may help if the gynecomastia is related to hormone imbalance, although they’re typically more effective in the early stages of the condition.
Exercise and Weight Loss: If gynecomastia is related to excess fat (pseudo-gynecomastia), weight loss may help reduce its appearance. However, true glandular tissue will not shrink through weight loss alone.
When to Consider Having Surgery
For persistent gynecomastia that doesn’t respond to non-surgical treatments, surgery can offer a long-term solution. Some men can have true gynecomastia (breast tissue) while others can have pseudo-gynecomastia (mainly fat), but there are some cases where it’s a combination of both breast tissue and fat. There are several surgical techniques available that can be tailored to effectively remove the excess tissue.
Liposuction: Liposuction can effectively remove excess fatty tissue, which may be enough to treat milder cases of gynecomastia. Small incisions are made in the armpit, and a thin tube (cannula) removes fat through suction.
Mastectomy (Excision): For men with significant glandular tissue, an excision may be required to remove glandular breast tissue directly. This is especially common in cases with excess skin.
Combination of Liposuction and Excision: Many patients benefit from both liposuction and excision, achieving a smooth, natural contour for the chest.
Anesthesia Options
Depending on the severity of the area, gynecomastia can be under under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. At Washingtonian Plastic Surgery, is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure comfort and a pain-free experience. However, for smaller procedures or in cases where only liposuction is required, local anesthesia with sedation may be an option.
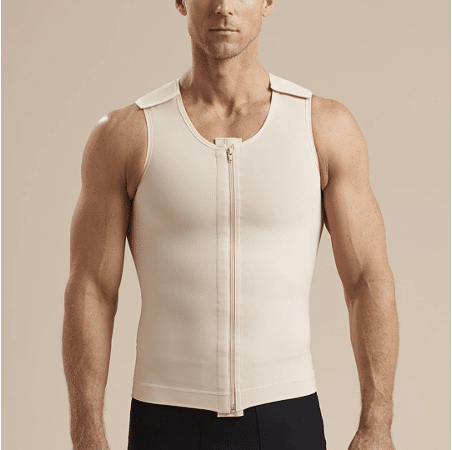 Compression Garments: Use and Types
Compression Garments: Use and Types
Post-surgery, a compression garment is essential for supporting the healing process. Here’s what to know:
Type: A snug, specially designed post-surgical vest or binder is usually recommended. It provides even pressure and supports the newly contoured chest.
Duration: Patients typically wear the garment continuously for the first few weeks, around the clock, gradually decreasing wear time as healing progresses. On average the
Benefits: Compression garments help reduce swelling, minimize fluid buildup, and encourage the skin to conform to the new chest contours.
Recovery Expectations and Timeline
Recovery from gynecomastia surgery varies, but here’s a general timeline:
First Few Days: Some pain, swelling, and bruising are normal during the initial days of recovery. Prescription pain medications or over-the-counter options can help with discomfort.
Gradual Return to Activity: Light activities can usually be resumed within a few days, but exercise, especially anything targeting the chest muscles, should be avoided for 4- 6 weeks.
Ongoing Compression Wear: Wearing the compression garment as directed is vital to the healing process and can enhance the final result.
Visible Results and Full Healing: While initial results are noticeable within 3–6 weeks as swelling reduces, full healing and the final contour may take several months.
Long-Term Results and Maintenance
The results of gynecomastia surgery are generally permanent, provided a patient maintains a healthy lifestyle. Gaining weight or using substances that affect hormone levels can cause the condition to recur, so a balanced lifestyle is key to maintaining the chest contour.
Gynecomastia surgery is transformative not only for the body but also for self-esteem. With Washingtonian Plastic Surgery’s guidance, men can find relief from the discomfort of gynecomastia and enjoy the confidence that comes with a firmer, more masculine chest contour.
If you’re considering surgery, consult with Dr. Navin Singh a board-certified plastic surgeon to discuss your options and create a personalized treatment plan that meets your needs and lifestyle. Click here to schedule your consultation today.



